How to Select the Right Coaxial Attenuator for Your Needs?
Selecting the right Coaxial Attenuator is crucial for optimal signal management in various applications. A coaxial attenuator reduces transmission signal strength and prevents interference. The process of choosing the right one can get complicated.
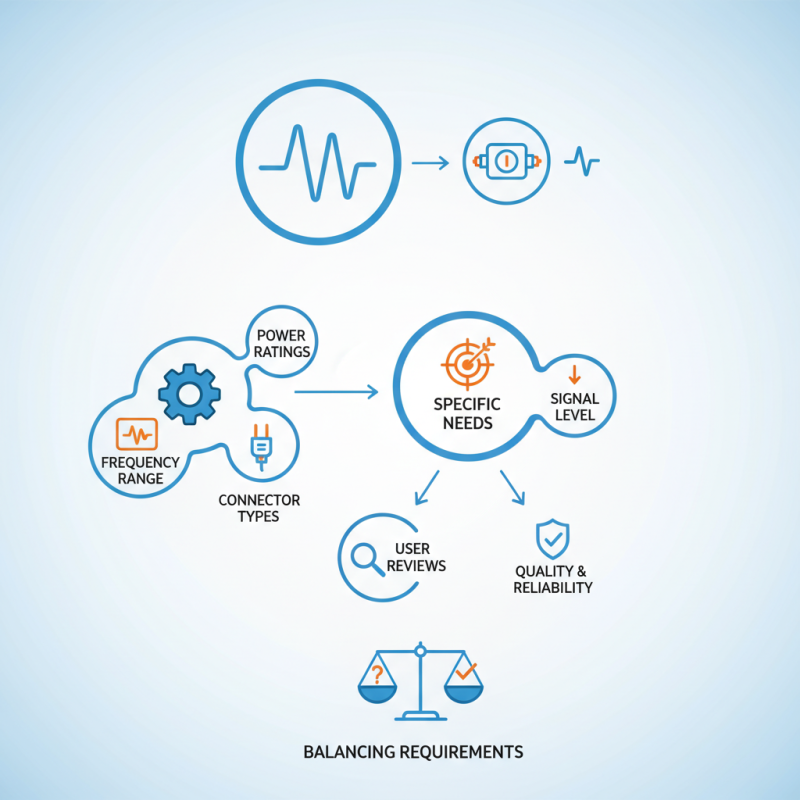
When looking for a coaxial attenuator, consider the frequency range. Different attenuators work best at specific frequencies. Attention to detail in specifications can save you time and frustration later. Additionally, pay attention to power ratings and connector types. These factors can significantly affect performance.
Think about your specific needs. Are you aiming to achieve a specific signal level? A mismatch here may hurt overall system performance. Balancing your requirements with the options available may require adjustments. Sometimes, the perfect fit isn't clear, and reflection on user reviews may help. Quality and reliability matter, but they can vary widely.
Understanding Coaxial Attenuators and Their Functionality
Coaxial attenuators play a crucial role in various radio frequency applications. Their primary function is to reduce signal strength without distorting the signal. This helps ensure that devices operate within their optimal range. Understanding how they work can lead to better choices for your needs.
Choosing the right coaxial attenuator depends on various factors. You need to consider the frequency range of your system. Different attenuators are designed for specific frequencies. This is vital to avoid signal loss and maintain performance. Pay attention to the dB rating as well. This indicates the amount of attenuation provided.
**Tips:** Always match the attenuator's type with your connectors. Impedance should also be a key consideration. Using a mismatched attenuator can lead to further issues. Check the power rating to ensure it can handle the signal levels in your setup.
Real-world testing can reveal imperfections. Sometimes, attenuators might introduce unwanted noise. Thus, it’s important to evaluate performance in your specific environment. Don’t hesitate to adjust based on your observations. The best results often come from trial and error.
How to Select the Right Coaxial Attenuator for Your Needs?
| Type | Frequency Range (MHz) | Attenuation (dB) | Power Rating (W) | Connector Type | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fixed Attenuator | DC - 1000 | 3, 6, 10 | 1 | N-Type | General RF Applications |
| Variable Attenuator | 10 - 4000 | 0 - 20 | 2 | BNC | Test Equipment |
| Digital Attenuator | 1 - 2000 | 1 - 31.5 | 0.5 | SMA | Telecommunications |
| RF Attenuator | 0 - 3000 | 6, 12 | 5 | TNC | Broadcasting |
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an Attenuator
When selecting a coaxial attenuator, consider several key factors. The frequency range is crucial. Ensure the attenuator can handle your desired frequency. Mismatched frequencies can lead to signal loss.
Power rating matters too. Choose an attenuator that supports your device's power output. Underestimating this can cause overheating. Keep an eye on handling power; it should match or exceed your application needs.
Tips: Measure your system's signal levels before purchasing. Knowing these levels helps you select the right dB attenuation. Consider whether you need fixed or variable attenuation. Fixed is straightforward, while variable provides flexibility.
Lastly, assess the connector types. Ensure compatibility with your existing system. Connectors that don't match lead to more issues down the line. Trying to adapt them may not always work effectively.
Types of Coaxial Attenuators and Their Applications
When choosing a coaxial attenuator, understanding the types available is key. There are fixed and variable attenuators. Fixed attenuators provide a specific level of signal reduction. These are ideal for consistent applications. Their simplicity makes setup easier, but they lack flexibility.
Variable attenuators offer adjustable signal reduction. This allows users to fine-tune their signal levels as needed. They are great for testing and experimental setups. However, they can be more complex to use. You'll often have to dial in the exact setting for each use, which may lead to confusion.
When selecting an attenuator, consider the application. Some jobs require precise control, while others benefit from stability. Look at power ratings and frequency ranges as well. These factors influence performance. Not every attenuator fits all situations. Experimentation might be necessary. You may discover what works best through trial and error, which can be a learning experience.
Calculating Required Attenuation for Your Specific Use Case
When it comes to selecting the right coaxial attenuator, knowing your required attenuation is crucial. The attenuation level is measured in decibels (dB). For example, a system might need 10 dB of attenuation to avoid overloading. If your signal is too strong, it could distort the output. Many users overlook this calculation. They may choose an attenuator randomly, leading to suboptimal performance.
To calculate the required attenuation, first measure your input signal level. Ideally, this should be done with a power meter. If your signal is at +15 dBm and your desired output is -5 dBm, the calculation would be simple. Subtract the desired level from the input level. In this case, 15 dBm - (-5 dBm) equals 20 dB. Therefore, a 20 dB attenuator is needed. According to a 2023 industry report, nearly 30% of users fail to calculate needed attenuation correctly. This mistake can result in compromised signal integrity.
Attention to detail is vital when selecting. Users often choose based on price or availability instead of precise calculations. Consider the frequency range of both the signal and the attenuator. Mismatched frequencies can lead to unwanted effects, such as signal loss and distortion. Don't ignore this aspect. Achieving optimal performance requires careful evaluation of specifications. Trusting empirical data and measurement practices can greatly enhance reliability in your selections.
Installation Tips for Optimal Performance of Coaxial Attenuators
When installing coaxial attenuators, attention to detail is crucial for optimizing performance. First, ensure the attenuator matches the system's impedance. A mismatch can lead to signal loss or reflections. Research indicates that a 3 dB increase in attenuation can double the signal-to-noise ratio, impacting overall performance. Choosing the right connector type is equally important; common options include BNC, F, and SMA connectors.
Proper placement of coaxial attenuators is also key. Ideally, they should be positioned close to the input of your equipment. This minimizes unnecessary cable runs and reduces the likelihood of signal degradation. Reports suggest that signal integrity can decline up to 30% over long cable lengths. Maintaining a clean installation environment is vital; dust and moisture can affect performance.
Finally, always double-check the specifications of the attenuator. Not all models handle the same frequency ranges. A slight oversight here can hinder your system's efficiency. Taking these practical steps can significantly enhance the functionality and reliability of your signal chain.
