What is Plastic Injection Mold and How Does it Work?
Plastic Injection Mold is a vital component in the manufacturing process. It plays a crucial role in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods. This process allows for the creation of precise plastic parts quickly and efficiently.
The technology behind Plastic Injection Mold may seem complex. In reality, it involves injecting molten plastic into a mold cavity. This technique helps produce detailed shapes and designs. However, ensuring quality can be challenging. Minor mistakes in the mold design can lead to defects in the final product, affecting functionality and aesthetics.
Understanding Plastic Injection Mold is essential for businesses. The right knowledge can improve production efficiency and lower costs. Yet, many still struggle with the intricacies involved. Addressing these challenges requires a commitment to ongoing learning. Investing in better molds and processes can yield significant benefits in the long run.
Definition of Plastic Injection Molding and Its Significance
Plastic injection molding is a process used for producing parts by injecting material into a mold. This technique is significant for creating complex shapes with great precision. It is widely used in various industries, from automotive to consumer goods.
The process begins with heating plastic pellets until they become molten. This molten plastic is then injected into a mold under high pressure. Once the material cools, it solidifies into the desired shape. This creates consistent and replicable components, which is crucial for mass production. However, achieving perfect molds can sometimes be challenging. Minor defects can arise, affecting product quality.
Tips: Ensure that the mold design is optimized. Even small adjustments can lead to significant improvements. Regular maintenance of injection machines is vital. Neglecting this can cause operational issues. Pay attention to the plastic material’s properties as well. Knowing their behavior affects the final product’s durability and finish.
Key Components of a Plastic Injection Mold
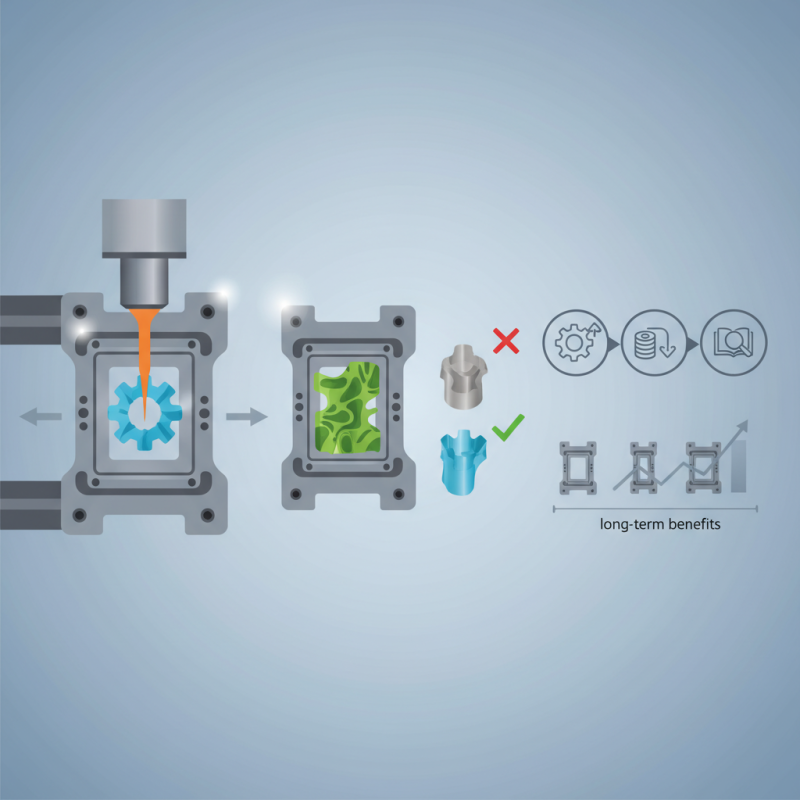
Plastic injection molds are critical in manufacturing plastic products. Understanding their key components is essential for efficient production. The mold primarily consists of two halves: the cavity and the core. The cavity shapes the outer surface of the product, while the core forms the inner parts. Together, they create the final design.
Another important aspect is the runner system. This system channels liquid plastic from the injection unit into the cavity. It can be a simple or complex network of channels. Designers must consider the flow to ensure even filling. Furthermore, the cooling system is also essential. It helps solidify the plastic quickly. However, improper cooling may lead to defects or warping.
It's worth noting that achieving perfect molds can be challenging. Small design flaws can lead to significant production issues. Even minor adjustments in temperature or pressure can impact quality. Manufacturers must continuously refine their processes. Regular testing and evaluation are necessary to enhance mold performance and reduce waste.
The Injection Molding Process: Step-by-Step Breakdown
Injection molding is a popular manufacturing process. It transforms plastic pellets into finished products with precision. The process involves several key steps.
First, plastic granules are heated until they melt. This molten plastic is then injected into a mold. It fills the spaces within the mold, taking its shape. Cooling follows, solidifying the plastic. Finally, the mold opens, and the finished product is ejected.
**Tip:** Pay attention to temperature settings. Too high a temperature can lead to poor quality. Cooling time is also crucial for achieving the desired strength.
Next comes inspection. Each piece is checked for defects. Not every piece passes inspection. Sometimes, adjusting the mold is necessary. Small changes can significantly impact quality.
**Tip:** Perform regular maintenance on molds. A well-maintained mold can enhance production efficiency. Do not overlook signs of wear or damage.
Throughout the process, maintain a clean environment. Contaminants can ruin the final product. Consistency is key in injection molding. Every step must be executed with precision for optimal results. Be ready to learn from mistakes.
Materials Used in Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding uses various materials, each tailored for specific applications. Common choices include thermoplastics and thermosetting plastics. Thermoplastics, like ABS and polycarbonate, are popular due to their flexibility and ease of processing. Reports show that thermoplastics account for over 70% of all plastic parts produced.
For functional and aesthetic parts, materials like nylon and polypropylene are often chosen. They provide durability and resistance to wear. Data from the Plastics Industry Association reveal that nylon's market is expected to grow by 5% annually due to its strength and lightweight properties.
Tips: Choose materials based on the final product's required strength and flexibility. Conduct thorough tests to ensure they meet performance standards. Remember, the right material can significantly impact production efficiency. Adjustments in material selection may lead to better outcomes. Always consider alternative materials that could reduce costs.
Common Applications and Industries Utilizing Injection Molding
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process. Many industries rely on it for creating parts. This method produces high-quality components efficiently. Common sectors include automotive, electronics, and consumer goods. Each of these fields requires durable, precise parts. For instance, the automotive industry uses it for dashboard elements and exterior components. Electronics often involve injection-molded casings for devices.
Healthcare is another significant user. Medical devices frequently utilize injection molding for their reliability. Examples include syringes, surgical tools, and housing for diagnostic equipment. The packaging industry also benefits. Containers and bottles are often made through this process. The results are lightweight, strong, and cost-effective products.
Yet, challenges exist. Maintaining quality can be difficult. Slight variations in temperature can affect the outcome. Manufacturers must ensure the consistency of materials. Moreover, not every design is suitable. Complex shapes may need tweaking. These hurdles require ongoing reflection and improvement in practices.
